
Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to automatically identify and classify assets and objects in mediafiles can enhance the Digital Asset Management (DAM) workflow in several ways, while also providing more accurate and useful information about the assets.
Everywhere you turn, for the past months, you hear people discussing how incredible OpenAI's newly unveiled ChatGPT model is. Will the rapid AI development and the awareness of it's powers affect DAMs and how and what kind of AI can enhance digital asset management?
Yes, for sure metadata can be ingested using AI, and this input can be useful to automate classification and move media files to specific user groups. It can save time and effort in organizing and managing digital assets.
DAM - AI is getting smarter
Computer Vision, like tagging and face detection, has been added since years as an external service to the DAM, although mostly predicting and adding only general, and often useless keywords to the system.
Read our blog: This is why AI assisted keywording only occasionally fits as part of DAM workflows
DAM vendors are now working on additional features that will harness the power and functionality to take its digital asset management services to the next level. Here are a few possible features for you to consider, at least if your DAM-vendor is able to offer any of these features:

- Automated tagging: AI can be used to automatically identify objects in images and tag them with relevant keywords, making it easier to search and find specific assets. AI can analyze the image content, such as visual elements, colors, and shapes, and assign tags that accurately describe the image and help to make the images more discoverable and searchable within the DAM system.
- Automatic categorization: AI can be used to automatically classify images based on the objects they contain, making it easier to organize and browse assets in the DAM system. For example, image recognition algorithms can be used to automatically extract keywords and captions from image files based on their content. Similarly, speech-to-text algorithms can be used to generate transcriptions and keywords from audio and video files.
- Facial recognition: AI can be used to automatically identify and tag people in images, making it easier to search for and find specific individuals. This can help to automatically identify and tag individuals within an image and by that support GDPR workflows and privacy regulations, which is useful for organizations such as in law enforcement, but also media companies and all kind of businesses with security needs and privacy issues. AI can be trained not only on individuals but also on groups of people. If the AI is ever unsure about the recognition of a person, it will suggest the most likely persons and you have to decide manually.
- Object detection: AI can be used to automatically identify and classify objects within images such as cars, buildings, products, animals, vehicles, or buildings etc. This can be useful for organizations that need to quickly categorize and sort large collections of images, such as a stock photo library. Often this supports the ability to recognize brands and their products to be classified automatically. This can also help in automating the process of making a catalog of products.
- Quality control: AI can be used to automatically identify defects or errors in images, and flag them for manual review and remove low-quality images from their DAM system, saving storage space and improving the overall performance of the system. An AI-based image analysis can be used to assess the quality of images, by analyzing the technical attributes of the image such as blurriness, resolution, lighting, and sharpness.
- Automatic captioning: AI can be used to automatically generate captions for images based on the objects they contain, making it easier to understand the context and usage of the assets. This AI-generated metadata can then be used to automatically classify and organize media files.
For example, files with certain keywords or captions could be automatically moved to specific user groups or folders based on their content. This can significantly improve the efficiency and organization of a digital asset management system, and make it easier for users to find the files they need. -
Automatic cropping: AI can be used to automatically crop images to focus on specific objects, making it easier to use assets in different contexts and publishing platforms. Smart cropping analyzes the composition of the image and how 'interesting' the different parts of it are. After that it automatically suggests what is the best region to crop, in order to preserve the most relevant part of the image!
-
Similarity search: Be it via visual similarity search, through automatic keywording or with the help of color search: the perfect image is only a few clicks away. AI also detects duplicates upon uploading.
Ingesting metadata using AI this way can greatly enhance the automation and organization of a digital asset management system and make the usage more user-friendly and making search and collaboration more accurate and easy.
Best arguments for always ingesting metadata in DAM
Here are some arguments for always ingesting metadata while uploading mediafiles into a digital asset management application:
- Improved organization: By including metadata with media files, such as keywords, captions, and descriptions, it is much easier to search for and locate specific files within a digital asset management system. This improves the overall organization and efficiency of the system.
- Enhanced discoverability: When metadata is included with media files, it becomes much easier for others to discover and use those files. For example, if a video file includes keywords that accurately describe its content, it is more likely to be found by someone searching for that type of content.
- Better collaboration: Metadata can also be used to track the history of a file, including who created it, who last modified it, and what changes were made. This information can be incredibly valuable when collaborating on a project and is useful for communication and coordination.
- Measuring performance: With metadata, it's possible to track the performance of media files and measure their impact. Metrics like views, clicks, shares, and engagement can help to understand the performance of media files, which can be used to improve the overall strategy and approach of digital assets
- Legal compliance: Certain industries and organizations have legal requirements for the handling of certain types of files and information. For example, certain image files need to have certain metadata to be used for medical research. Ingesting metadata during upload ensures compliance with these legal requirements.

AI moves from single- to multitasking
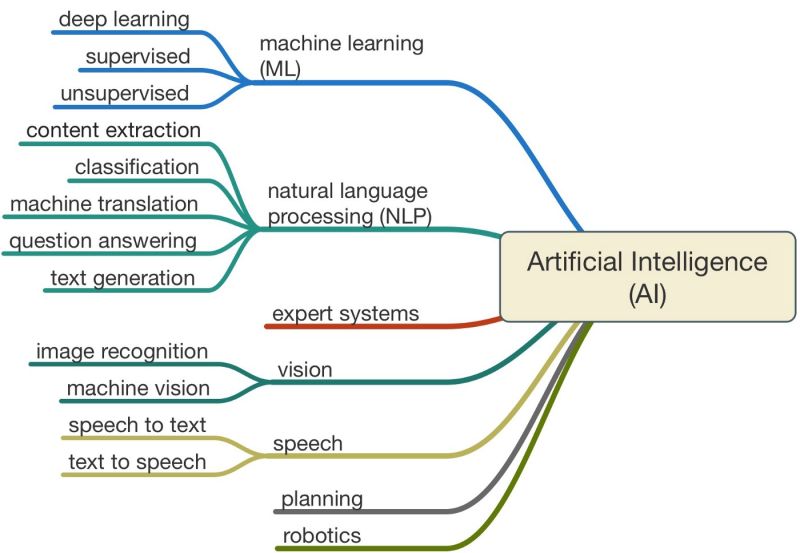
AI tools are no longer working separately for only one task. Object, voice and facial recognition combined with text search can not only find a video, it enables to find the precise moment somewhere inside a video. By combining computer vision to classify images, OCR to extract any text from the image and NLP used for text classification, businesses can utilize content in different ways. NLP (Natural language processing) is in content management the big trend since ChatGPT was introduced in late 2022 and the latest version GPT-4 was unveiled by OpenAI on March 14, 2023.
Please find more on ChatGPT in DAMs later in this article.
There are a few different ways how artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to classify media files in a DAM:
Computer vision: AI algorithms can analyze the visual content in a mediafile, such as objects, people, scenes, and other features, to classify the file based on its content. This can be done using techniques such as image and video recognition, object detection, and scene segmentation. Image captioning is a fundamental task in vision-language understanding, where the model predicts a textual informative caption to a given input image. An image or video library that tags itself!
Visual Search: Visual Search allows any user to easily organize, access, or recommend their images or products by keyword or visual similarity. User can perform powerful searches across your own collection of images using pre-built models or your own custom model.
Data labeling is the act of adding keywords to unstructured data, like video, images, audio, or text, so that machines learn to automatically recognise the concepts that these keyword describe. Advanced AI comprehends visual content and forms a human-like descriptive sentence by choosing each word in the phrase from a flexible vocabulary.
Image Classification: Classification is the most popular image recognition technique in commercial use today. When a user takes a photo, they receive a list of keywords and a percent likelihood for each keyword’s applicability to the image based on their observational bias. AI can be used to classify images based on their content.
For example, an AI model could be trained to identify whether an image contains a cat, a dog, a person, or something else. AI can detect duplicates and related assets. It can recognize similar images and automatically populate the same set of metadata across related assets. For the automatic classification of images, an individual custom model of a artificial neural network is trained with the customer's inventory data. Images are parsed through, analysed and suggested which categories they represent.

Audio Classification: AI can be used to analyze the audio content and classify audio files based on their content. For example, an AI model could be trained to identify whether an audio clip contains music, speech, or noise. It can also analyze the audio content of media files, such as audio recordings or music tracks, to identify specific sounds or musical features. This can be used to classify the files based on genre, mood, or other characteristics.
Video Classification: A neural network can watch and understand videos and tell you what it´s seeing. AI can be used to classify video files based on their content. For example, an AI model could be trained to identify whether a video clip contains a person speaking, music playing, or a scene from a particular movie. AI can analyze the visual content of media files, such as images and videos, to identify objects, people, scenes, and other features. This can be used to categorize the files based on their subject matter or content.
AI offers major enhancements for video services by adding and supporting subtitles, and much more. It thereby ensures that the solution complies also with WCAG 2.1 AA to make sure everybody, even disabled persons can enjoy the videos easier and turns the videosto be accessible.
Text Classification: AI can be used to classify text files based on their content. For example, an AI model could be trained to identify whether a piece of text contains news, sports, or entertainment content. AI can analyze the text content of media files, such as captions or transcriptions, to identify key words and phrases. This can be used to categorize the files based on their topic or theme. Detecting and extracting text within an image, with support for a broad range of languages, along with support for automatic language identification is becoming very useful. Read more on how ChatGPT can help classifying textual objects later in this blog.
Hybrid approaches: AI algorithms can also be used to classify videos by combining multiple approaches, such as analyzing the visual, audio, and text content of the video. This can provide a more comprehensive and accurate classification of the video.
Advancements in technology have made document processing possible in DAMs. With the capabilities of content intelligence technologies like machine learning (ML) and optical character recognition (OCR), document capture and processing can now be integrated directly into processes.
Using Named Entity Recognintion (NER) technology you can identify and classify named entities in text data, such as organisations, people and locations, making content understanding easier. Organisations can extract meaningful insights from their unstructured data.
Your predictive models learn everything they need from your training datasets. This data must be accurately labeled and consistent with real-world conditions. Your AI gets and is only as good as your training data.
It is important to note that Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems can produce bias if they are not properly build, implemented trained and tested. Bias can occur in the data used to train the AI, in the algorithms used, or in the way the AI is used in the workflow.
Organizations must be aware of the legal issues surrounding the use of AI to scan visual files and generate metadata for digital asset management systems, and to take steps to comply with all applicable laws and regulations for example to obtain consent from individuals before collecting or using their.
Discuss with the DAM-vendor on how deep the integration of AI has been implemented in Your DAM and whether it actually gives you enhancements in your work.
How to utilize AI in your DAM
Aimed at creating business value in an AI assisted DAM workflow means at least turning unstructured information (documents, images, audio, video, etc.) into structured data, making all information searchable and actionable.
Before thinking of implementing AI solutions into your own specific DAM environment every corporate needs to identify what problem AI could solve and what kind of AI services are needed to make that happen.

As we implement AI into a DAM, we need to be careful to do so in a way that makes asset metadata more meaningful, not less, so that DAM administrators can make assets more easily discoverable.
Maybe this is what you might want to solve in your DAM workflow: improve efficiency, predict something, find something etc. Next you need to ask have you got the relevant data to be used in an AI-model? How will this affect affect the people and the workflows in the organisation?
Organisations who use DAM solutions are very particular about their keywords and taxonomies. They need a visual recognition solution that is not only accurate but also adaptable to its customers’ needs. This mostly means specific model training.
Custom data models deliver more meaningful outcomes
For example, by training a custom machine learning model on a large dataset of labeled media files and metadata, the model can learn to generate metadata that is accurate and consistent across a wide range of media files. Custom models deliver more meaningful outcomes for the business. AI enables organizations to describe their assets in the context of their business which is much more meaningful than generic tags.
From a DAM perspective this means being able to locate the right image at the right time for the right use case. The more you know about an asset and what it contains the more useful it becomes. As many brands have unique taxonomies and keywords they want to use, the next stage is to make the technology even more personalized for clients’ unique needs through custom models and tags. i.g to personalize AI to fit their specific needs and build AI into their workflows.
New concepts can be trained with high accuracy much faster than before, requiring less than 25 images per concept as compared to the thousands of images per concept traditional AI training required. And, with each new image example, the AI will get smarter and better at recognizing your concept! The new models can be generated easily, even in some cases with non-experts. The effort depends strongly on the customer's objects to be trained. The training process is preferrably though actively performed by an AI engineer.
Generative AI and ChatGPT will change the workflows
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence that can generate novel content, rather than simply analyzing or acting on existing data. Gen-AI is a way of creating content that doesn’t exist yet and marketing teams have a lot to gain from this. No topic in the world of technology is attracting more attention and hype right now.

Text-to-image AI models generate detailed original images or paintings based on simple written inputs. By teaching the AI how to recognise what’s in an image, like hundreds of pine trees, it is then able to replicate its own tree, combining it with other elements it has learned about. Text-to-image tools are producing and creating images, paintings and videos using trained algorithms.
Creating the perfect image for your marketing content in just seconds will become handy. An image generator tool integrated in DAM is the future for DAM and a suitable tool to manage all versions of this content, no doubt. These AI models can create images, videos, and interactive media based on textual descriptions or other inputs.
How to deal with AI generated Images, GDPR etc.? Image-generating softwares using artificial intelligence like ChatGPT4, DALL-E2 and Midjourney allows infinite creative combinations of images, all based on a written prompt. These creations need to be validated by humans and descriptions of the image should manually be edited, to state how it has been created. This guarantees that the outputs are legally clean and safe for any commercial usage.
It will be important for organizations to carefully consider tracking and managing generative AI-created content. A transparrent way would be to label all generative AI-created content in a DAM system and to use separate metadata fields to store this information. This way you are able to properly manage and protect assets and its use. There are several other ways to deal with labelling of generative AI-created content in DAMs.

Image DALLE-2: Create a painting of a troubadur with beard singing and playing guitar on an old sailingship.
AI-powered text generation, like Open AI:s ChatGPT, may essentially create more value than AI-powered image generation. Machines’ ability to generate language, to write and speak, will prove to be extremely transformative. AI-generated language will probably transform the way that every company in every sector in the world works.
Open AI ChatGPT is one of the first true applications for generative text, in terms of commercial adoption. It has proven to be copywriting which referres to AI-generated website copy, social media posts, blog posts and other marketing-related written content. And this is just the beginning of adoptions and applications. As more players will come soon, one thing that would give more trust in Generative AI is if the source of the original information was mentioned by the AI.
GPT-4 is a large multimodal model, it is able to accept both text and image inputs and output human-like text. Not only can GPT-4 produce more natural-sounding text and solve problems more accurately than its predecessor. The new model can interpret and output longer blocks of text: more than 25,000 words at once. It can also process images and videos in addition to text meaning it can process and respond to the visual inputs it receives. ChatGPT has strong abilities in coding. You can use it as a designer tool. Create a following webpage and make it as a HTML page including text and images.
Some enhancements are also likely to happen within the workflows in a DAM like ways you can crop, edit and optimise formats with AI. Here are a few to look at:
- Dynamic resizing and formatting for responsive design
- Image retouching and blemish removal
- Color correction and enhancement for visual assets
- Focal point cropping for image composition
- Background removal for product images
- Video clipping and trimming for social media posts
- Noise reduction and enhancement for audio files
- Audio transcription and captioning for accessibility
Now it is all about how AI could be smart integrated in DAM systems.
Read our blog: ChatGPT, an alternate way of working for writers and content creators?
GPT AI for metadata processing in DAMs
DAM vendors can incorporate the GPT-language model for metadata processing in DAMs to improve efficiency, accuracy and creativity. With this integration DAMs can be configured with tasks to automatically process metadata. Simply by configuring a prompt on an output metadata field, and selecting an input field to use as the source, DAM can automatically generate the output field's value.
Her are just a few examples - as the prompts are entirely user configurable, there are potentially unlimited applications for metadata processing.
Automated title/summary generation: DAMs can be configured to generate concise and descriptive titles and summaries from large blocks of text, such as extracted from a PDF file, subtitles from a video file, or pulled in from another system.

Keyword extraction: DAMs can automatically extract meaningful keywords from a block of text, providing a list of relevant keywords for searching, categorization, and more. The list of keywords can be made more specific based on the prompt provided.
For example, if a user uploads a photo of a mountain landscape, the language model could generate a metadata description that includes keywords like "mountain," "landscape," "nature," and "scenic view." This could save time and improve the consistency and accuracy of metadata tagging.
Creation of a keyword tree with the help of ChatGPT can also give you a controlled vocabulary, which is very important for keywording and metadata optimization.
Automatic categorization: GPT integration can be used to automatically categorize digital assets based on their content, saving time and ensuring consistent and accurate categorization. ChatGPT can be used to create a content-specific metadata schema that is suitable as a starting point for professional digital asset management.
Improve Image Descriptions: With GPT-4’s image recognition capabilities, DAM platforms could automatically generate rich descriptions for uploaded images. Given appropriate prompts, the ability to understand and describe images means GPT-4 could also suggest relevant copy or captions to accompany visual assets. It could analyse images and video frames to detect explicit or harmful content and thereby flagging this content.
Improve Accessibility: ChatGPT can help to make digital products more accessible by generating alternative text for images or creating captions for videos. The organisation may set a goal for the design team to use ChatGPT to improve the accessibility of the product, ensuring that it can be used by all users, regardless of their abilities.
Improve Searches: Another possible use case for ChatGPT in DAMs is to provide natural language search capabilities, as mentioned earlier. Users could enter a natural language query, such as "find photos of mountains with blue sky," and the language model could parse the query and return relevant search results.
How will digital asset managment transform in this new reality?
Done right, these new capabilities using AI-technologies may save hours of administrative time in the business-wide organisation of marketing, managing files and videos. It gives next-gen marketers the ability to automate and streamline daily processes. It will also create new jobdescriptions as well as a lot of new applications. What the new ChatGPT4 with its new abilities can do in DAMs will probably change the whole way how to search, archive and produce context and information. This enhancement promises better categorisation, metadatageneration, content creation, and search capabilities, leading to an overall improvement in DAM systems. To go further, it can recommend to a prompt content for the user because it understands the content and context.

DALL·E 2023 - Create an image of the techno hype of AI in a communicative manner.
AI Visual Search
AI Visual Search is a service that allows users to search their entire library for assets based on visual descriptions recognized by AI, making it easier and faster to find the right image for a specific application. A key benefit of AI Visual Search being metadata-less is the removal of any manual tagging requirements of image contents, an extremely time-consuming and human error-prone task.
AI Visual Search uses language and image recognition to intelligently match search terms to visual qualities, removing the need for asset tagging.
Generative AI may change the way searches are performed in Digital Asset Management (DAM) systems, providing more relevant search results. By better understanding the content and context of the assets being searched for makes the process easier for users to find the content they need.
Generative AI is a topic that will come up more and more in DAMs. There is a desire to adopt generative AI in DAMs, but also fear that generative AI is a black box that creates answers that aren't grounded in business data. When this is combined in business organisations with siloed AI initiatives and top-down pressure to adopt AI, the situation can get worse.
The impact of generative AI on the content stored in DAM systems will depend on how the technology is used and the goals of the organization. The specific tools and implementation strategies will depend on the needs of the organization and the nature of the digital assets being managed.
While these exciting new technologies make it easier for businesses to produce high-quality content at record speeds, building and scaling up an AI-powered content strategy involves considering more than output. You need to strategise for the entire content lifecycle and learn how to leverage AI technology. In the process, businesses and workflows will be transformed dramatically.
Look for a modern DAM to manage content
DAM-systems need to integrate AI services deep into their data models, metadata schemas and workflows to enable efficient classifications of content and by this turning unstructured information (documents, images, audio, video, etc.) into structured data, making all information searchable and actionable.
Expectations for artificial intelligence in general is high, but what is actually going on at DAM vendors. The gap between ambition and execution is large. ChatGPT and similar AI-technologies has finally opened the mind of most DAM and SaaS vendors, making integration of sophisticated AI-solutions more efficiently a necessity. AI will for sure be one of the definitive evolutions of the future of digital asset management.
As DAM vendors start adopting personnalized machine learning and visual recognition technologies in order to stay innovative and competitive in the market the integrated algorithms will help to better take advantage of and describe the content. Artificial intelligence will add value to digital content.
How will DAM vendors integrate these new, more powerful AI tools into their technologies? We hope, that they will do more than what they did earlier with automated tagging, meaning the minimum required to enable them to tick the Generative AI box (autotagging box) without much thought for how their end users can usefully apply it. In the end the quest is how this will impact the way we manage our digital assets and our operations in the coming years.
In terms of implementing ChatGPT in DAM systems, it's important to note that the language model is not a turnkey solution and will require customization and training to work effectively with a particular DAM system. Additionally, there are considerations around data privacy and security when using AI tools that need to be taken into account.
So lets wait for the impact of the new AI-driven game-changing digital asset management applications of tomorrow.
PS. This content was also partly assisted by Open AI ChatGPT.
As a leading service provider we offer expertise in digital asset management (DAM) and management of sophisticated solutions in a variety of business areas. Communication Pro helps to build and customize DAM, that will get easy to use.
Interested? Check out our DAM services here or book a online meeting here.
 |
Author Rolf Koppatz Rolf is the CEO and consultant at Communication Pro with long experience in DAMs, Managing Visual Files, Marketing Portals, Content Hubs and Computer Vision. Contact me at LinkedIn. |
